Nick Wood
London
Altra Motion, the North American motion control company, has recently made a strategic investment into the advanced manufacturing software company, MTEK Industry. The investment is another in a long string of acquisitions or strategic investments witnessed in the wider motion control sector - symbolic of a wider market shift towards greater industrial automation, a focus on advanced manufacturing and the continued adoption of robotics.
While the robots may grab the headlines, the motion control industry is the real driving force behind them. A motion control system is typically comprised of three components: a controller, a drive, and a motor, which work in conjunction to power a larger system, such as a robot.
Oxford Economics estimates that the number of robots will increase from 2.25 million in 2019 to 20 million by 2030. As a result of a prime end-market growing, the supplying motion control market is also projected to enjoy strong growth in the coming years:
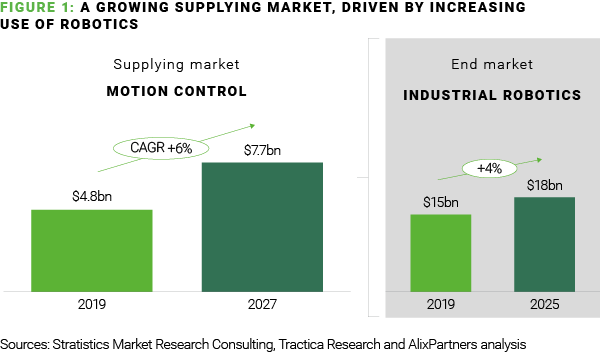
Driven by this global megatrend, the motion control sector has undergone significant shifts which have driven M&A strategies:
1. Increasing use of robotics – across all end-markets
The use of robotics goes far beyond industrial automation. Medical device machinery requires highly accurate, repeatable positioning in everything from CAT scanners to blood testing equipment. Agricultural drones and robots require precision when it comes to picking and sampling fruit.
Implications for M&A: This makes operators with expertise in high growth end-markets such as medical devices or robotics prime acquisition targets. Altra Motion’s $3bn acquisition of Fortive’s Automation & Speciality business to accelerate its growth in the medical, robotics and factory automation sectors is a key example.
2. Increasing customisation solutions
Driven by the complex nature of the systems that motors power, we have seen an increasing demand from the industry’s customers to have customisable, specialised motion control products. This is often to meet regulatory requirements, where systems need to be FCA-approved before going to market.
Implications for M&A: Smaller players with unique R&D capabilities or a customisation focus can command interest from larger buyers, with MOONS’ purchase of Yunkong Electronic in 2018 underlining this trend.
3. Machine designer needs
Driven by the ongoing need to improve manufacturing efficiency and cost reduction, machine designers continue to push for smaller, quieter and more reliable components or smarter technologies.
Implications for M&A: In order to grow market share or to secure increased share of customer spend, existing players in the motion control space are using M&A as a means to broaden capabilities or access to know-how. ABB’s investment in Canada’s Planar Motors Inc. (PMI) is a recent example. The strategic partnership will give ABB access to PMIs magnetic levitation technology which is deployed in smart conveying robot systems.
With strategic players continuing to pursue acquisitions as a means of achieving growth or enhanced capabilities, combined with the motion control industry’s growth dynamics, highly specialised operators and exposure to regulated end-markets, the willingness to pay strategic premiums has pushed up business valuations across the sector. This, combined with the billions of dollars of private equity money raised to capitalise on the increasing convergence of manufacturing and technology is likely to continue to fuel activity and growth in the sector. The robots are here!